Toby Perrett, Alessandro Masullo, Tilo Burghardt, Majid Mirmehdi, Dima Damen
University of Bristol
Abstract
Meta-learning approaches have addressed few-shot problems by finding initialisations suited for fine-tuning to target tasks. Often there are additional properties within training data (which we refer to as context), not relevant to the target task. These can act as a distractor to meta-learning, particularly when the target task contains examples from a novel context not seen during training.
We address this oversight by incorporating a context-adversarial component into the meta-learning process. This produces an initialisation which is both context-agnostic and task-generalised. We evaluate our approach on three commonly used meta-learning algorithms and four few-shot case studies: character classification with alphabets as context, image classification with superclasses as context, bird classification with colour as context and calorie regression from video with participants as context. Our context-agnostic meta-learning improves results in each case.
Context in Few-shot Problems
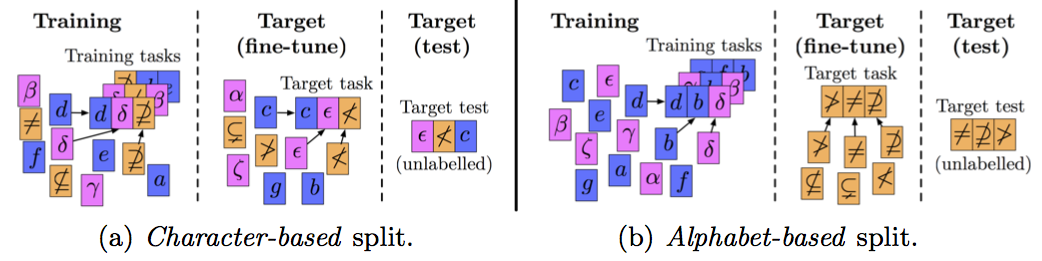
Here are two few-shot learning experimental setups for a character classification problem. In this case, context information is the alphabet label, shown in colour. Note that the context could be one or more other cues, such as author, font, etc. The alphabet-based split, where context is shared between the train and test sets, is easier than the character-based split, as a meta-learner may become distracted by the alphabet during training. We target splits where context is not shared between the train and test sets.
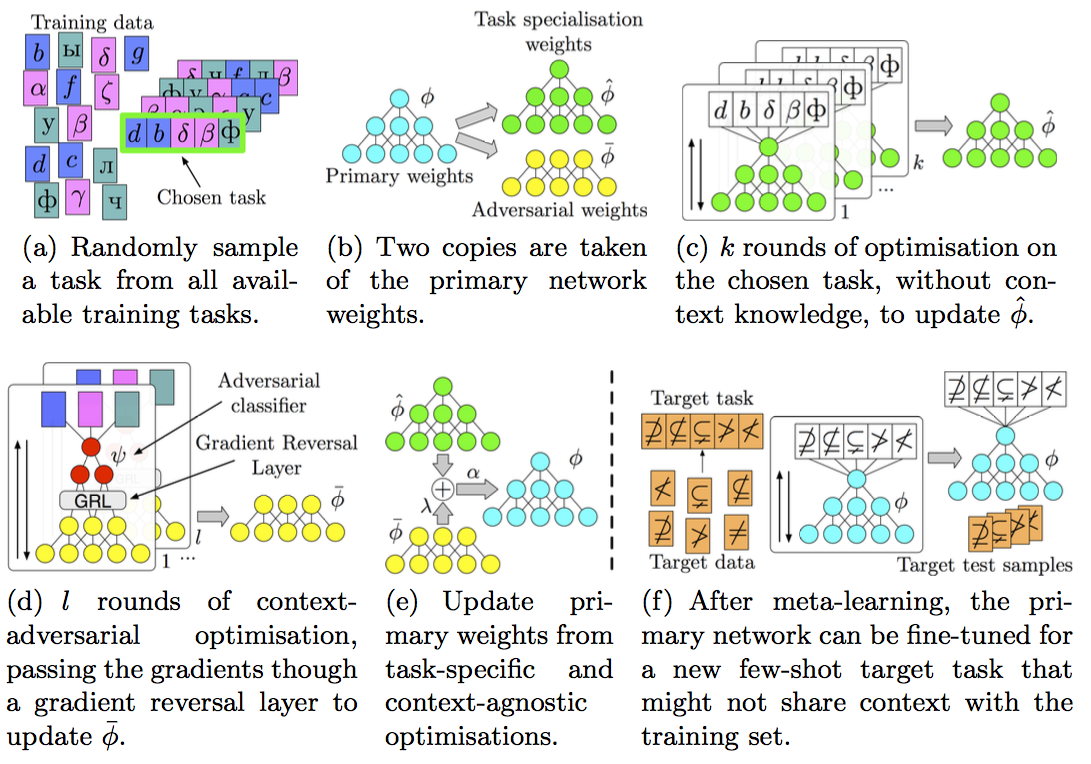
Method
Video
Paper
Bibtex
@InProceedings{perrett2020meta,
author = {Perrett, Toby and Masullo, Alessandro and Burghardt, Tilo and Mirmehdi, Majid and Damen, Dima},
title = {Meta-Learning with Context-Agnostic Initialisations},
booktitle = {Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV)},
year = {2020}
}